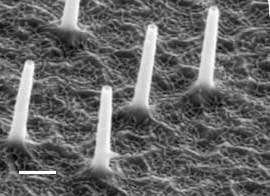
Wednesday, October 31, 2018
Nanostraws deliver molecules to human cells safely and efficiently
Flexy, flat and functional magnets
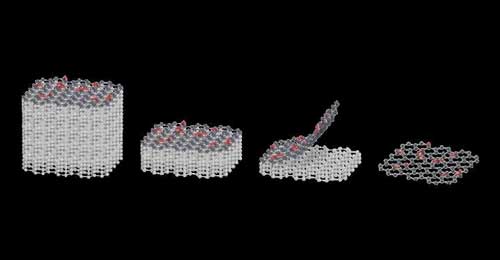
2-D magnetism: Atom-thick platforms for energy, information and computing research
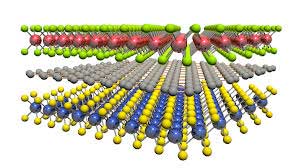
New digital tiles turn bedroom walls into cinema screens

Five minutes in the life of a molecular shuttle
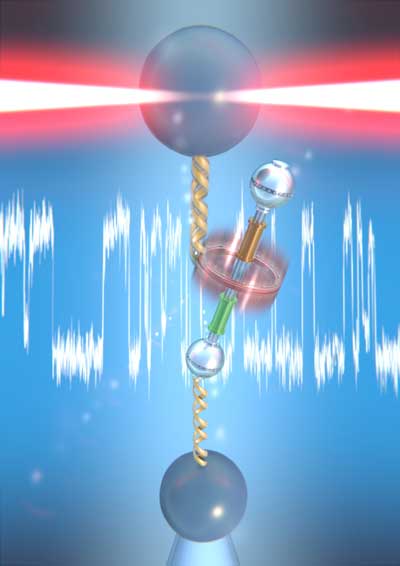
Eco-friendly waterproof polymer thin-films synthesized using novel method
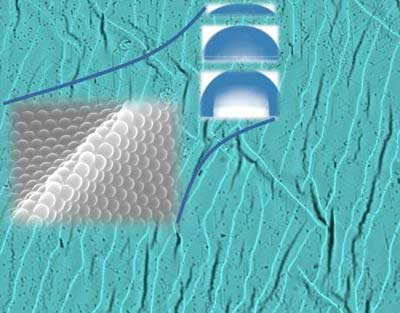
Ultrasensitive toxic gas detector
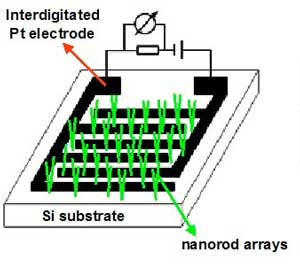
A bullet-proof nanowire heating pad
Laser-activated silk nanosealants outperform sutures for tissue repair
Bose-Einstein condensate generated in space for the first time

Don't underestimate the force
Tuesday, October 30, 2018
Making a transparent flexible material of silk and nanotubes
Nanowire-based light detectors work like gecko ears

Tiny, pain free vaccinations - microneedles and nanoparticles
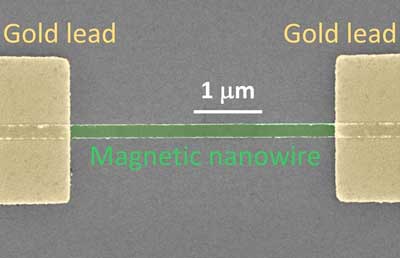
Scientists discover technique for manipulating magnets at nanoscale
Crystal size of organic semiconductors can be controlled using inorganic polymer micropillar-based solution shearing system
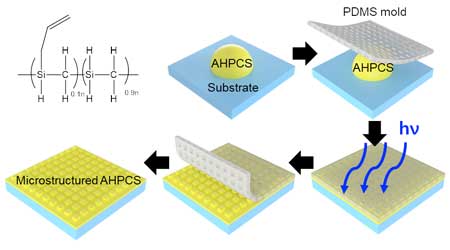
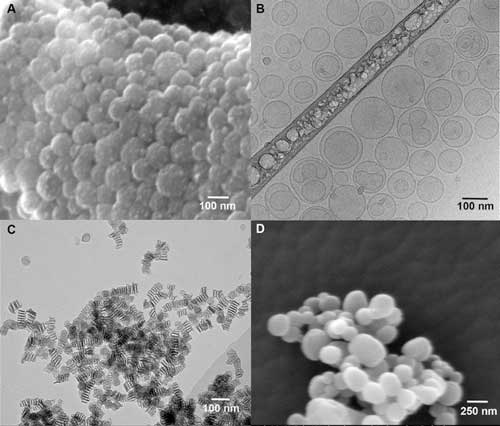
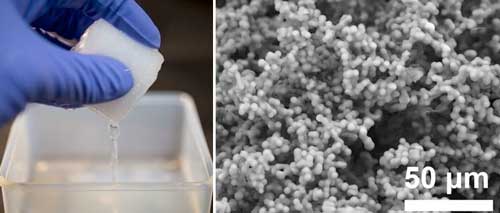
Simple, mass production of giant vesicles using a porous silicone material
Monday, October 29, 2018
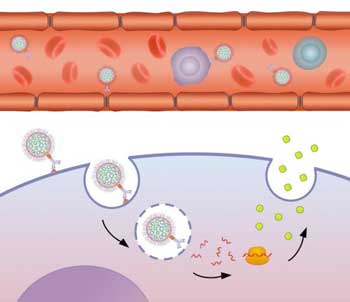
New platform based on biology and nanotechnology carries mRNA directly to target cells
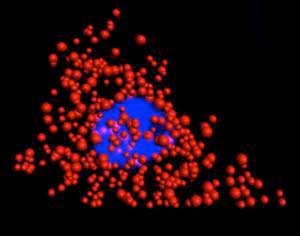
Novel quantum dots enhance cell imaging
Researchers create scalable platform for on-chip quantum emitters
AI and NMR spectroscopy determine atoms configuration in record time
A USB stick? In the distant future, a little powder should suffice

First single-photon source that works with atomic gases at room temperature
New composite material that can cool itself down under extreme temperatures

Friday, October 26, 2018
Delivering pressure with an unconventional crystal interface
Highly efficient wet-processed solar cells with molecules in the same orientation
Scientists form atomically flat tellurium

Researchers switch material from one state to another with a single flash of light
Nanocrystals arrange to improve electronics
Photonic plasmon hook: scientists obtain a new class of curved beams for biosensors and nanoparticle control
A self-powered heart monitor taped to the skin

Scientists create new oil-resistant filter technology (w/video)
Thursday, October 25, 2018
Spinning the light: The world's smallest optical gyroscope

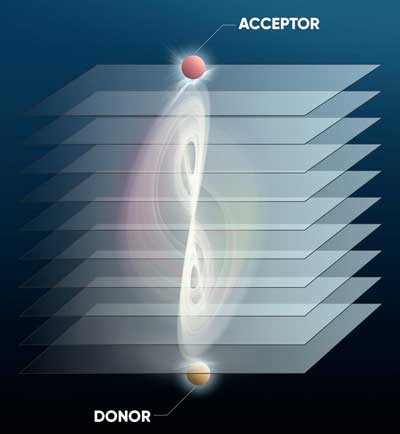
Study breaks Förster resonant energy transfer (FRET) distance limit
Nanotubes may give the world better batteries

Light-bending tech shrinks kilometers-long radiation system to millimeter scale
Wednesday, October 24, 2018
Researchers discover directional and long-lived nanolight in a 2D material
Revealing the mechanisms behind the enhancement of thermal properties of graphene nanofluids
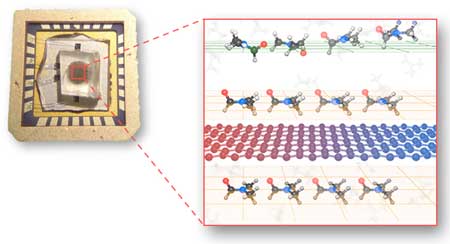
Nanophotonics technology to allow 100-times-faster internet
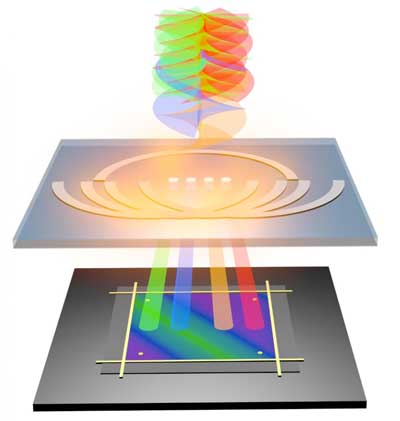
Probing electronic properties to engineer new materials
Wood sponge soaks up oil from water

Just in time for Halloween: Brain-eating amoebae halted by silver nanoparticles
Researchers design 'smart' surfaces to repel everything but targeted beneficial exceptions

Tuesday, October 23, 2018
How to mass produce cell-sized robots

'Mushrooms' and 'brushes' help cancer-fighting nanoparticles survive in the body
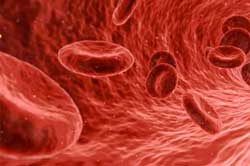
A molecular sensor for in-situ analysis of complex biological fluids
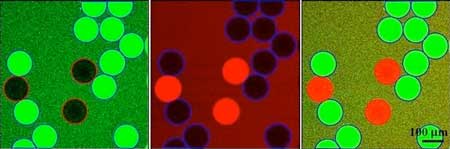
Mussel-inspired defect engineering enhances the mechanical strength of graphene fibers
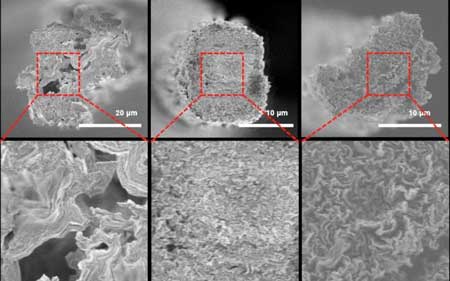
Deformation of nanotubes to control conductivity
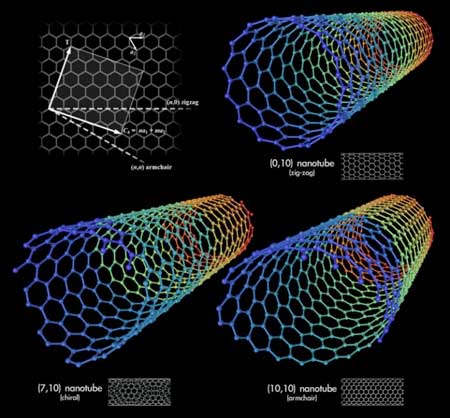
Where deep learning meets metamaterials

Extremely thin, stable, and bright: 2D materials for the photonics of tomorrow
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
